这些基础的东西在官方文档里面都有详细的说明 http://nginx.org/en/docs/
其实 nginx 的文档还不错,下面讲的这些在文档里面都有详细的讲解
nginx 中的指令都可以在这个 官方页面 中找到
nginx.conf 文件结构
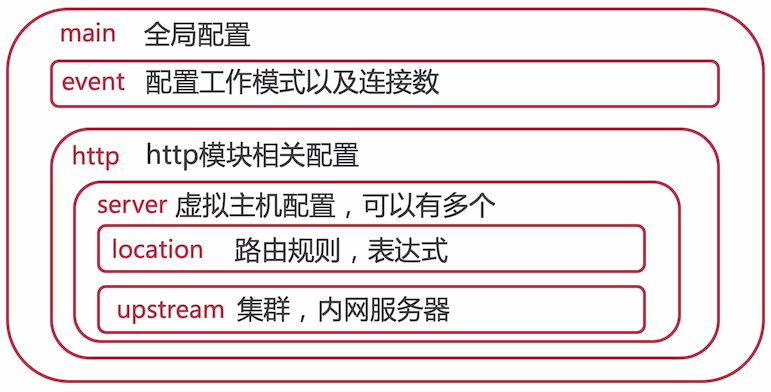
# 一条指令,由分号结尾
worker_processes 1;
# 花括号的为指令块,里面包含多个指令块
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
# 由 $ 符号开头的是 nginx 内置的一些变量
# log_format main '$remote_addr ....'
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# 指令之间由至少一个空格进行分割
# 也可以使用 tap,一个 tap 表示 8 个空格,但是一般使用 4 个空格缩进比较好
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
指令详解
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
user
user nobody:由操作系统的哪一个用户来执行指令
worker_processes
配置几个 worker 服务,一般配置为 CPU 核心数,或则未核心数 减 1
error_log
配置错误的日志,文件后面的为日志级别
error_log logs/error.log;
error_log logs/error.log notice;
error_log logs/error.log info;
日志级别从低到高分别是:debug、info、notice、warn、error、crit
默认日志文件地址在我们安装的时候通过 --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/xx.log 指定了,我们不配置的话,它自己也有默认文件地址的
pid
运行时的进程 ID 文件
events
events {
# 默认使用 epoll,在 linux 下最合适的就是 epoll,其他平台上可能不一样
use epoll;
# 每个 worker 允许连接的客户端最大连接数
worker_connections 1024;
}
http
网络传输相关的模块,是一个指令块
include
include mime.types;
在 nginx.conf 同级目录下,有一个 mime.types 文件,里面也是一个指令块内容,包含了很多的 mime type
同理,include 就可以导入你自己的其他配置文件了,通过它来进行分类重用之类的工作
log_format
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
需要配合 access_log 使用,log_format 是日志格式的指定,记录的是 http 请求相关的日志信息
[root@study conf]# cat /var/log/nginx/access.log
192.168.56.1 - - [04/Apr/2021:16:32:44 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36"
192.168.56.1 - - [04/Apr/2021:16:32:44 +0800] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 555 "http://192.168.56.105/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36"
如上所以的日志格式,就是被注释的默认格式所格式化出来的
● remote_addr:ip 地址
● remote_user:远程用户,一般都是横杠 - 表示无法获取
● time_local:访问时间
● request:访问方法和地址还有协议
● status:响应状态
● body_bytes_sent:响应内容的大小
● http_referer:用是从哪一个链接跳转过来的
● http_user_agent:用户代理,一般写的浏览器
● http_x_forwarded_for:客户端 IP,通过代理转发后的 IP
sendfile
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
文件高效传输,而 tcp_nopush 需要配合 sendfile 一起使用,含义是:当数据包内容累积到一定大小的时候才会发送,相当于是定义缓存
keepalive_timeout
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
客户端链接服务端超时的时间,http 协议里面的东西,保持长链接的空闲时间,这里单位是秒
gzip
#gzip on;
gzip 压缩开关
server
server 也就是虚拟主机
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
● listen:监听端口
● server_name:可以定义 IP 或则域名
● location:路由
● error_page:发生错误的时候,使用这里响应的状态码页面展示
配置 Nginx 为静态资源提供服务
发布静态资源作为一个服务,供用户使用
我们可以这样做,创建一个 /usr/local/nginx/conf/my.conf 的文件,里面写指令,再在默认的配置文件里面 include 进去,分离我们自己的脚本文件的方式来组织配置
my.conf
server {
listen 90;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
index index.html;
}
}
以上配置,我们将我们前端项目使用 nginx 部署了,这个时候可以访问 http://192.168.56.105:90/ 就能访问到前端项目了
另外还可以将图片等文件配置成服务,比如 /home/foodie-shop/images 下有很多图片
location /images{
root /home/foodie-shop;
}
这种方式需要注意的是:root + location + 请求的资源链接起来要是一个主机上存在的物理路径。
那么还可以使用 别名(alias) 的方式进行映射,如下所示
# 配置路由规则
location /i2 {
# 资源所在的物理路径
alias /home/foodie-shop/images;
}


